In recent years, medical record-keeping has evolved into a science that is increasingly using computers and digital technology to fulfill the needs of clinicians, researchers, administrators, legal regulatory agencies, and insurance companies. Medical records are important because ‘people forget and record remembers’. The Medical Records Department, which is entrusted with the storage, analysis, and retrieval of records, plays a vital role in management, planning, medical audits, policy decisions, and research in our institution. Further, the information provided by this department to the health authorities of the city, state, and country forms the basis on which several health-related decisions are taken at those levels. The Medical Records Department (MRD) at SGRH is one of the best in the country, having meticulously followed well-established procedures ever since its inception and having updated them regularly, including the use of Information Technology.
A medical record is defined essentially as a document that supplies:
1. A basis for the continuity of patient care;
2. A fundamental means of communication among healthcare personnel;
3. A source of comparative studies and research;
4. A medium of education for medical and paramedical personnel; and
5. A legal protection for institutions, practitioners, and patients.
According to McGibony, a chronicle of the pageantry of medical and scientific progress is found in hospital records. In SGRH, the record is source-oriented and is divided into sections such as the physician’s notes, laboratory reports, and nurses’ notes. The entries in each section are arranged in chronological order. The MRD plays a vital role in management, planning, medical audits, policy decisions, and research. The statistics generated by the department act as a catalyst in the process of healthcare and quality management.
The MRD of our hospital assures high-quality services and complies with the guidelines of certifying bodies such as the National Accreditation Board for Hospitals and Healthcare Providers (NABH) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO). In a recent NABH reassessment audit, the department was acknowledged as one of the best departments of the hospital. It also received appreciation from the Government of India for efficiently implementing the coding of diseases according to ICD-10 in the second review meeting for improving and strengthening of ICD-10 and Medical Records System in India by the Central Bureau of Health Intelligence at the National Institute of Health and Family Welfare (NIHFW), New Delhi.
In SGRH, the MRD was started in the basement near the radiology department in the year 1976. At that time, the bed strength was 140 and there were about 15 admissions per day. With the increase in the number of beds and the subsequent increase in the number of admissions. At present the bed strength is 560 (as per DHS Registration) with 250–260 admissions per day. The Records department spreads over an area of (25×37) 925 square feet and is spread over two levels, including the internal and satellite storage space outside the hospital premises at Todapur, Inderpuri, New Delhi.
The overall responsibility for the efficient functioning of the department is that of the Director of Medical Dr (Brig) Satendra Katoch. However, the department functions under the direct supervision of the Senior Medical Record Officer, Mrs. Puja Singh, who is responsible for all the work of the department. She has been given authority commensurate with the responsibility assigned to her.
On 18 June 2007, with the implementation of the Hospital Information System (HIS), the activities of the department were computerized. Most of the census, hospital statistics birth and death reporting, government-notified data, and all communicable and non-communicable data are being done by using the computer.
HIS attempts to integrate and communicate all the investigations to the patient through the online and easy flow of information within the hospital. The HIS has helped the MRD enormously, as :
1. Coding of all diagnoses is done through the HIS-Trackcare.
2. Due to the unique ID number, tracking a patient’s disease and treatment is possible.
3. Data extraction and analysis are immediate.
4. Demographic analysis is automated.
5. Reports are generated to provide information to government authorities, e.g. notification of diseases.
6. Retrieval of reports is possible an infinite number of times as the data is stored permanently.
The objectives written in the department’s manual are:
1. To collect and preserve medical records for easy retrieval of healthcare information.
2. To index and code diseases and operations as per ICD-10.
3. Qualitative and quantitative analysis of health records: To develop and maintain an information base and mechanism for providing statistical data.
4. To control the movement of records for maintaining confidentiality.
5. To comply with medico-legal aspects and the related statutory laws of the country.
6. To provide records for research work.
7. To cooperate with the medical, nursing, and other departments in order to obtain comprehensive patient records and to design and develop effective medical record forms.
8. To continuously strive for innovations to improve departmental functions.
9. To develop educational programs for medical record personnel.
1. Receiving, checking, coding, indexing, assembly, and storage of all medical records of discharged patients, with a discharge analysis.
2. Maintaining birth and death data, along with notification of all communicable and non-communicable diseases, report for Integrated Disease Surveillance Project, Urban Disease Surveillance Project, etc., to the public health authorities.
3. Making the census on a daily basis, preparing monthly abstracts, and recording annual hospital statistical details.
4. Maintaining medical records permanently for Death/MLC cases; 3 years for general cases and 3 years for casualty cases.
5. Making records available for medico-legal purposes, presentation in a court of law, research, and inquiries from the Life Insurance Corporation regarding disease and cause of death of the insured.
6. Verification of hospitalization particulars, for issuing various certificates, including medical certificates.
7. Upgradation of the forms used in the hospital.
8. Collection and computation of information from other sources, including health services.
All patient and non-patient-related data and information generated, provided, or contained in the hospital shall be kept appropriately confidential, integrated, and secured. All information concerning a user, including information relating to his/ her health status, treatment, or stay in the hospital, is confidential, and is to be treated as such no person may disclose any information contemplated unless –
• The user consents to that disclosure in writing;
• A court order or any law requires such disclosure; or
• Non-disclosure of the information represents a serious threat to public health.
Without prejudice to the generality of this section, special precautions for the maintenance of confidentiality shall be taken, with respect to –
• Persons affected with HIV/AIDS;
• Persons with mental health problems; and
• Persons in danger to national security or to society.
Patient records shall be kept confidential in SGRH, complete and secure both in manual and electronic form. This shall be in accordance with the Indian Evidence Act, Indian Penal Code, and Code of Medical Ethics. These records shall be safeguarded against loss, destruction, and tampering. Adequate space, cleanliness, and storage furniture shall be maintained in the Medical Records Department. Privileged health information shall be used for the purposes of medico-legal cases only. Patients/physicians and other public agencies requesting access to medical records shall be done as per the Document.
Hospital statistics are prepared on a monthly, quarterly, half-yearly, and annual basis, as follows, and submitted to the management.
The graphical charts are based on year-wise analysis.
1. Total admissions/discharge report-monthly/daily.
2. Average outpatient attendance per day.
3. Specialty/doctor-wise operations.
4. Inpatient sex ratio.
5. Bed occupancy rate.
6. Average length of stay.
7. Birth rate/mortality rate/infant mortality rate/maternal mortality rate.
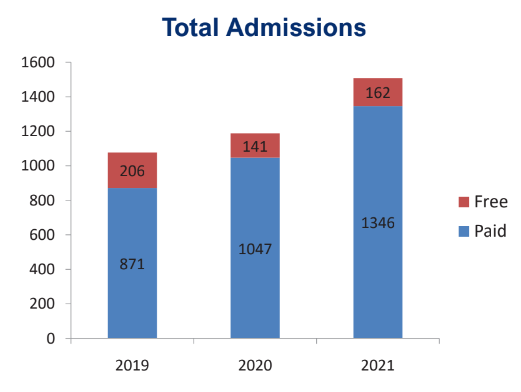
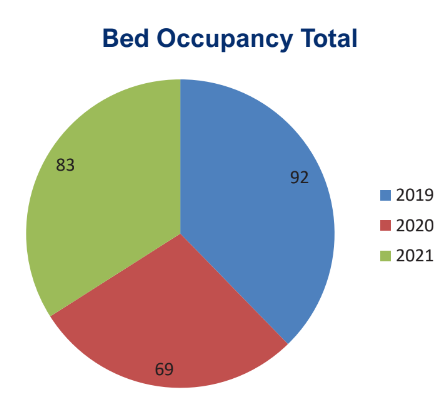
The reports including notifiable diseases that are submitted to the Delhi administration are as follows.
1. Weekly/monthly/yearly/SOS reporting of the following: Viral fever, measles, cholera, gastroenteritis, malaria, dengue, blindness control, leprosy, neonatal tetanus, poliomyelitis, snake bite, kala-azar, meningitis, cancer, cataract surgeries, hydrophobia.
2. Weekly reporting of cases/deaths due to Japanese encephalitis, AFP surveillance.
3. Compilation of report of hospital morbidity and mortality according to the ICD.
4. Report of births and deaths.
5. Cases and deaths due to communicable diseases.
6. Weekly integrated disease surveillance project, urban disease surveillance program.
7. Monthly/SOS maternal death report.
8. Daily/SOS swine flu report.
A systematic approach is ensured by a quality assurance plan, which allows for objective analysis of services through the use of pre-established criteria to monitor the adequacy of medical records documentation. The quality assurance program of the department involves the following steps:
• The formation of a medical records committee to ensure that quality service is provided by the department through continuous monitoring of its activities.
• Regular and continuous monitoring to ensure that documentation by the doctors and other staff is complete in all manner.
• Controlling the movement of records by adhering to the loan-out process.
• Ensuring the safety of records through various measures.
• Maintaining the documentation of destroyed records after the stipulated time period.
• Colour coding of forms for better compliance by the staff.
• Training at department levels where the head of the department takes training sessions for the technicians on a monthly basis.
• On-job training as per the need.
The MRD is an important department of the hospital and a nodal point for patients, doctors, researchers, medical administrators, and insurance companies. In SGRH, we have taken a step towards the computerization of admission, discharge, and the investigation sheet. However, much needs to be done for the full computerization of medical records, which is necessary to decrease the storage needs in a space-constrained institution such as ours. Technology such as microfilming will also help to reduce storage space.
1st Floor, HR Building, Ext: 1940/1942